The actual work of dispatching/sending an email is performed by an Email Service Provider (implements IEmailServiceProvider). Some providers requires settings, this can be implemented using a extension for the backoffice.
The package ships with four providers out of the box:
SmtpClient in System.Net.Mail.We also provide some open source implementations of providers that you can use in your project or use as a reference for your own custom implementations:
The Email Service Provider needs to be configured in the Administration-section for each Workspace.
Use some of the open source providers above as inspiration. Here is a simple example of a "empty" provider:
using NewsletterStudio.Core.Models.System;
using NewsletterStudio.Core.Notifications;
using NewsletterStudio.Core.Sending;
using NewsletterStudio.Core.Sending.Providers;
using Umbraco.Cms.Core.Events;
namespace Demo.Web.Extensions.EmailServiceProvider;
public class CoolEmailCompanyEmailServiceProvider : IEmailServiceProvider
{
private readonly IEventAggregator _eventAggregator;
public string Alias => "coolEmail";
public string DisplayName => "Cool Email";
public Dictionary<string, object> Settings { get; set; }
public CoolEmailCompanyEmailServiceProvider(IEventAggregator eventAggregator)
{
_eventAggregator = eventAggregator;
}
public SendOutConfiguration GetSendOutConfiguration()
{
return new SendOutConfiguration()
{
MaxItemsPerBatch = 10,
SendBatchSize = 10
};
}
public ErrorCollection ValidateSettings(Dictionary<string, object> settings)
{
var errors = new ErrorCollection();
var apiKeyValue = settings["cc_apiKey"]?.ToString();
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(settings["cc_apiKey"]?.ToString()))
{
errors.Add(new ValidationError("cc_apiKey","API key is required"));
}
if (settings["cc_apiKey"]?.ToString() == "lorem")
{
errors.Add(new ValidationError("cc_apiKey", "API cannot be lorem"));
}
return errors;
}
public async Task SendAsync(List<SendEmailJob> batch)
{
foreach (var job in batch)
{
var fakeDtoForEmailService = new
{
sendTo = job.Message.To,
body = job.Message.HtmlBody
};
// Fires the EmailSendingNotification to allow package consumers to make adjustments to
// the model before calling upstream services.
// This is optional for internal implementation but recommended if you plan to share
await _eventAggregator.PublishAsync(new EmailSendingNotification(fakeDtoForEmailService)).ConfigureAwait(false);
// Then send the email
//_coolCompanyEmailApi.Send(fakeDtoForEmailService)
var success = true;
if (success)
{
job.Successful = true;
job.ExternalId = "---id-if-provided-from-service";
}
else
{
job.ErrorMessage = "--error message---";
}
}
}
public async Task<CommandResult> SendAsync(EmailMessage message)
{
var fakeBulk = new List<SendEmailJob>();
fakeBulk.Add(new SendEmailJob() { Message = message });
await SendAsync(fakeBulk);
var res = fakeBulk.First();
if (res.Successful)
return CommandResult.Successful();
return CommandResult.Error(new ValidationError("", res.ErrorMessage));
}
}
Adding the Email Service Provider to our list of services, in your startup code:
using NewsletterStudio.Core.Composing;
using Umbraco.Cms.Core.Composing;
namespace Demo.Web.Extensions.EmailServiceProvider;
public class CoolCompanyComposer : IComposer
{
public void Compose(IUmbracoBuilder builder)
{
builder.NewsletterStudio().EmailServiceProviders.Append<CoolEmailCompanyEmailServiceProvider>();
}
}
Then, in the Workspace administration, the new provider should show up here:
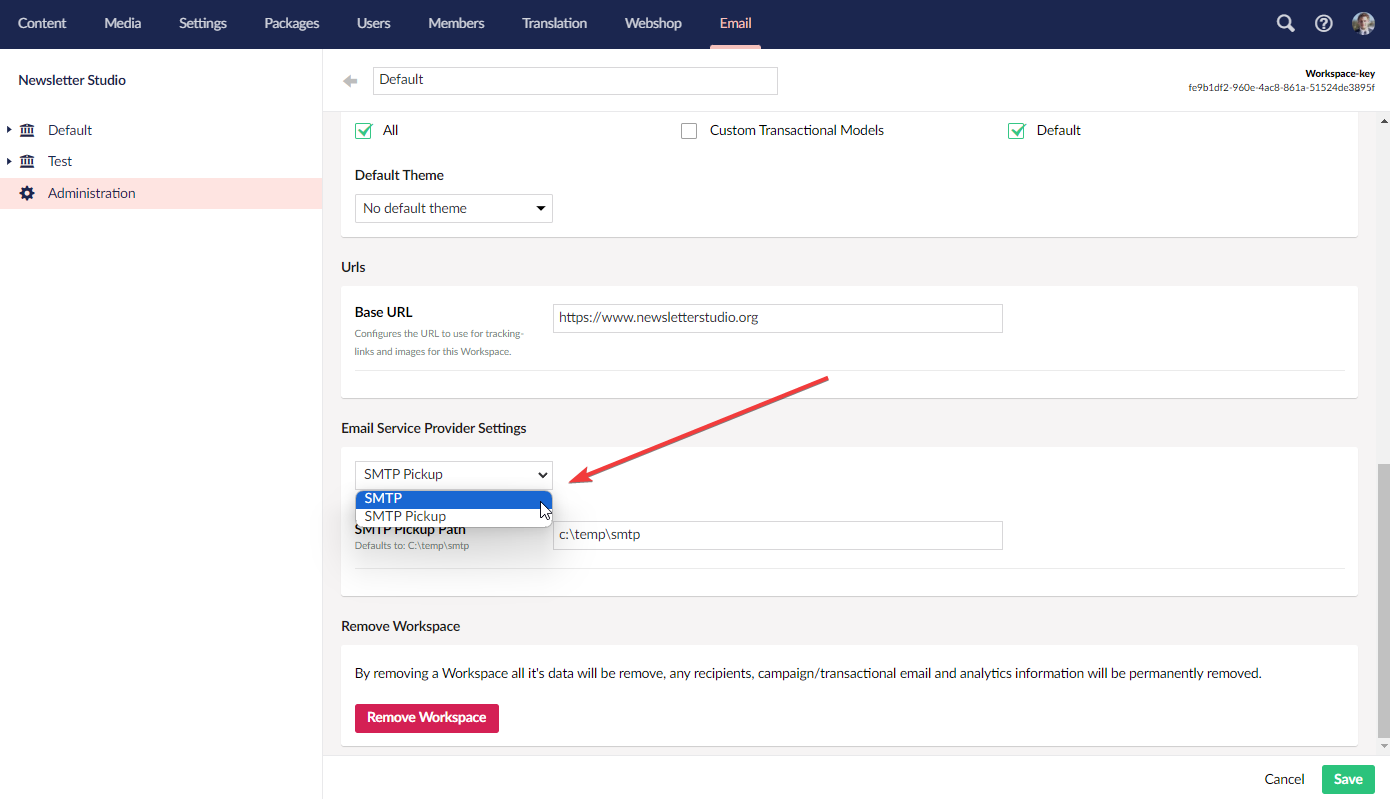
You can also provide an extension for the backoffice to mount a element for settings related to the provider.
First, create a element to render
import { UmbTextStyles } from '@umbraco-cms/backoffice/style';
import { css, html, customElement, state } from '@newsletterstudio/umbraco/lit';
import { NsEmailServiceProviderUiBase } from '@newsletterstudio/umbraco/extensibility';
import {NS_ADMINISTRATION_WORKSPACE_CONTEXT, NsAdministrationWorkspaceContext} from '@newsletterstudio/umbraco/administration';
import { umbBindToValidation } from '@umbraco-cms/backoffice/validation';
@customElement('cool-email-email-service-provider-settings')
export class CoolEmailServiceProviderSettingsElement extends NsEmailServiceProviderUiBase<CoolEmailServiceProviderSettings> {
#workspaceContext? : NsAdministrationWorkspaceContext;
@state()
workspaceKey? : string;
constructor() {
super();
this.consumeContext(NS_ADMINISTRATION_WORKSPACE_CONTEXT,(instance?) => {
this.#workspaceContext = instance;
this.observe(this.#workspaceContext?.workspaceKey,(workspaceKey) => {
this.workspaceKey = workspaceKey;
});
});
}
/**
* Notice the name renderSettings(), the parameter provided will be an object will all settings
* @param settings
* @returns
*/
renderSettings(settings : CoolEmailServiceProviderSettings) {
return html`
<ns-property
label="API Key"
description="Enter the API key for Cool Company" required>
<uui-form-layout-item>
<uui-input type="text"
.value=${settings.cc_apiKey ?? ''}
name="cc_apiKey"
@change=${(e:Event)=>this.updateValueFromEvent('cc_apiKey',e)}
label="API Key"}
${umbBindToValidation(this,'$.cc_apiKey',settings.cc_apiKey)}
required></uui-input>
</uui-form-layout-item>
</ns-property>
`
}
static styles = [UmbTextStyles, css`
uui-input {width:100%;}
`]
}
export default CoolEmailServiceProviderSettingsElement;
declare global {
interface HTMLElementTagNameMap {
'cool-email-email-service-provider-settings': CoolEmailServiceProviderSettingsElement;
}
}
interface CoolEmailServiceProviderSettings {
cc_apiKey : string;
}
Then register the element as a nsEmailServiceProviderSettingsUi extension.
import { ManifestEmailServiceProviderSettingsUi } from "@newsletterstudio/umbraco/extensibility";
const smtpCoolCompanyUi : ManifestEmailServiceProviderSettingsUi = {
type: "nsEmailServiceProviderSettingsUi",
name: "Cool Company Email Service Provider Settings",
alias: "Cc.EmailServiceProviderSettings",
element: () => import('./cool-email-email-service-provider-settings.element.js'),
meta: {
// this alias should match alias in IEmailServiceProvider-implementation
alias : 'coolEmail'
}
};
export const manifests = [
smtpCoolCompanyUi
]